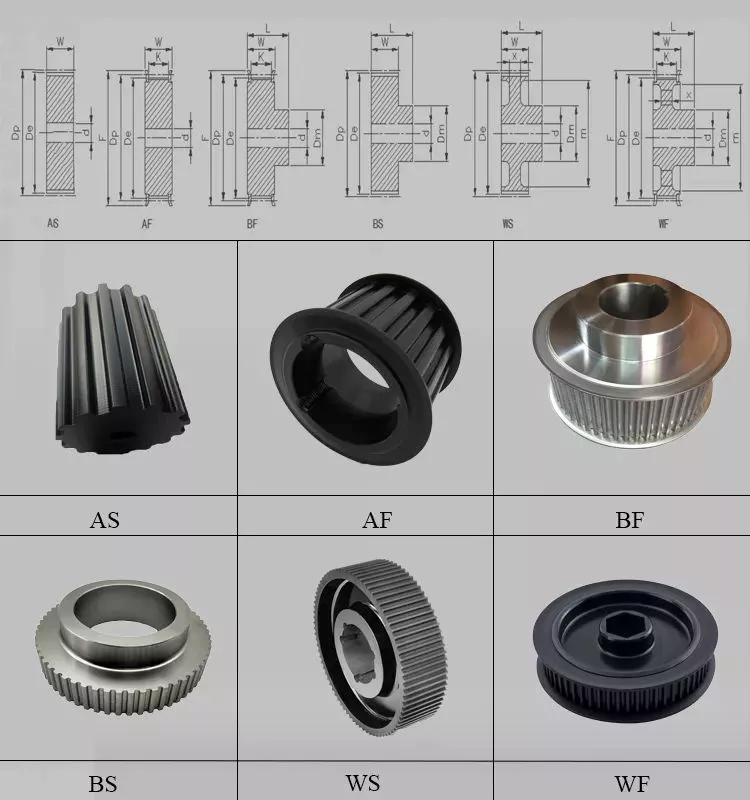
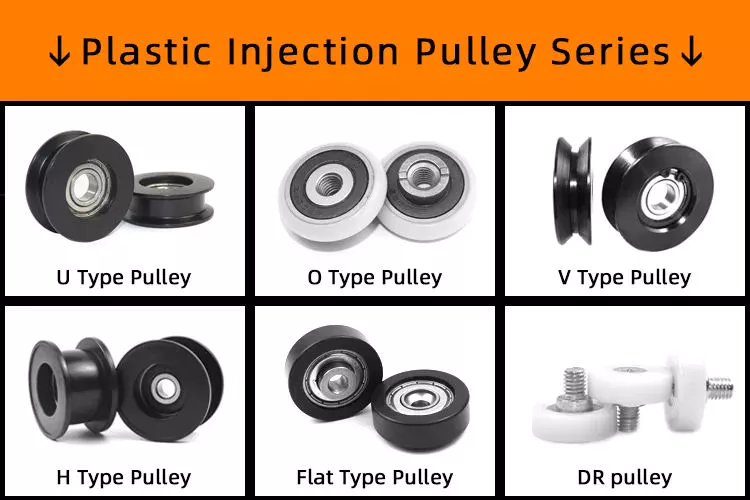
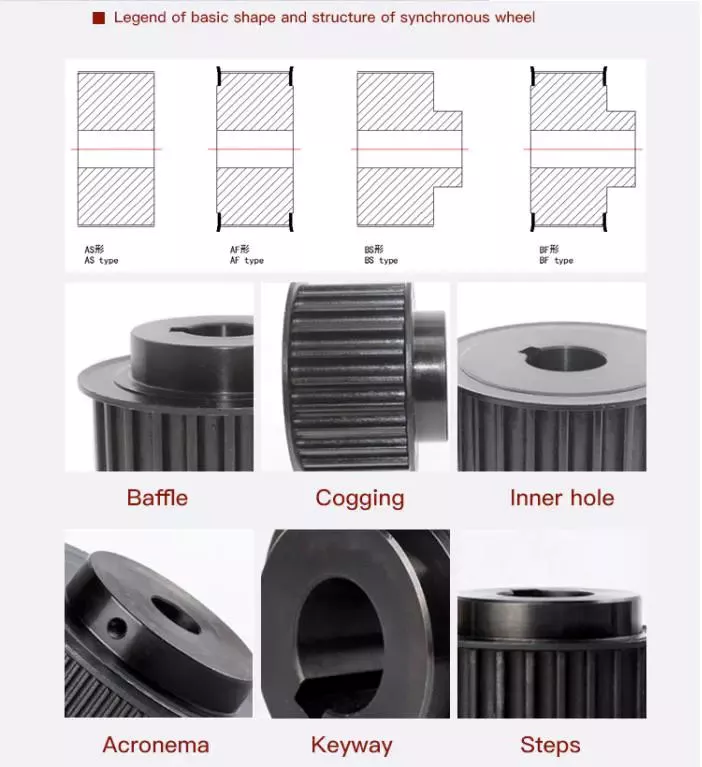
Product Description
Product Description
A conveyor will always consist of at least 2 pulleys, head pulley and tail pulley, with additional pulleys used depending on the configuration. Standard-duty pulleys are usually adequate for simple applications, but mine-duty and engineered pulleys are also available where heavy-duty pulleys are required.
Different kinds of conveyor pulleys
KONWEYOUR sells conveyor pulleys in all the following sub-categories:
Head pulleys
The head pulley is located at the discharge point of the conveyor. It usually drives the conveyor and often has a larger diameter than other pulleys. For better traction, the head pulley is usually lagged (with either rubber or ceramic lagging material).
Tail and CHINAMFG pulleys
The tail pulley is located at the loading end of the belt. It comes with either a flat face or a slatted profile (wing pulley), which cleans the belt by allowing material to fall between the support members.
Snub pulleys
A snub pulley improves the traction of the drive pulley, by increasing its belt wrap angle.
Drive pulleys
Drive pulleys, which can also be the head pulley, are driven by a motor and power transmission unit to propel the belt and material to the discharge.
Bend pulleys
A bend pulley is used for changing the direction of the belt.
Take-up pulley
A take-up pulley is used to provide the belt with the proper amount of tension. Its position is adjustable.
Product Parameters
| Type | Belt width(mm) | Standard Diameter(mm) | Length(mm) |
| Drive Pulley | 500 | 500 |
Length of the pulley depends on the belt width of the conveyor |
| 650 | 500~630 | ||
| 800 | 630~1000 | ||
| 1000 | 800~1150 | ||
| 1200 | 800~1150 | ||
| 1400 | 1000~1350 | ||
| 1600 | 1150~1600 | ||
| 1800 | 1150~1800 | ||
| 2000 | 1350~2000 | ||
| 2200 | 1600~2200 | ||
| 2400 | 1800~2400 | ||
| Bend Pully | 500 | 250~500 | |
| 650 | 250~630 | ||
| 800 | 250~1000 | ||
| 1000 | 250~1600 | ||
| 1200 | 250~1600 | ||
| 1400 | 315~1600 | ||
| 1600 | 400~1600 | ||
| 1800 | 400~1600 | ||
| 2000 | 500~1600 | ||
| 2200 | 630~1600 | ||
| 2400 | 800~1600 |
Packaging & Shipping
Detailed Photos
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
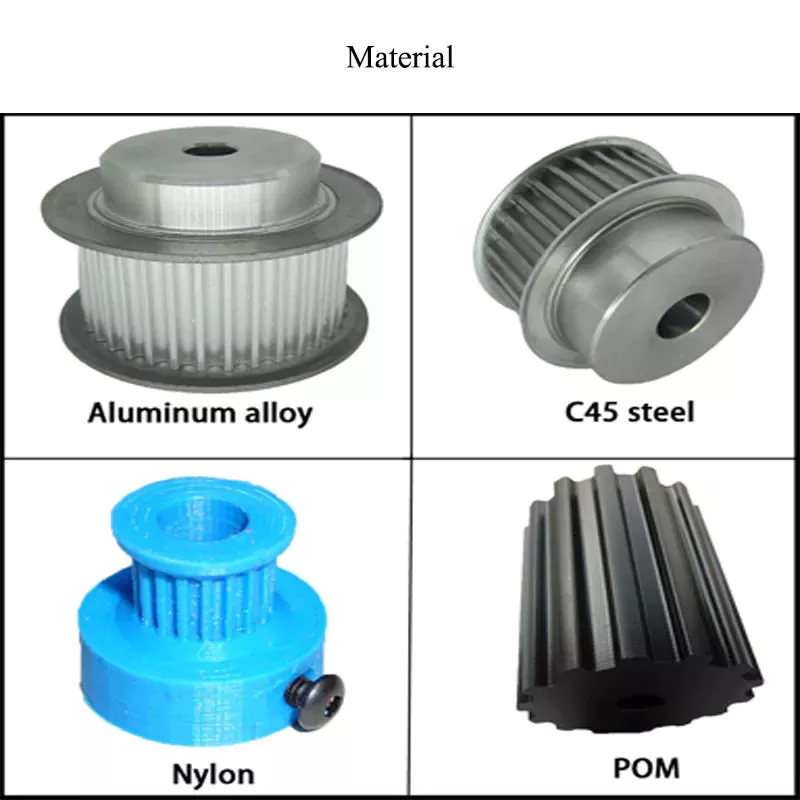
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
|---|---|
| Surface Treatment: | Baking Paint |
| Motor Type: | Frequency Control Motor |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|
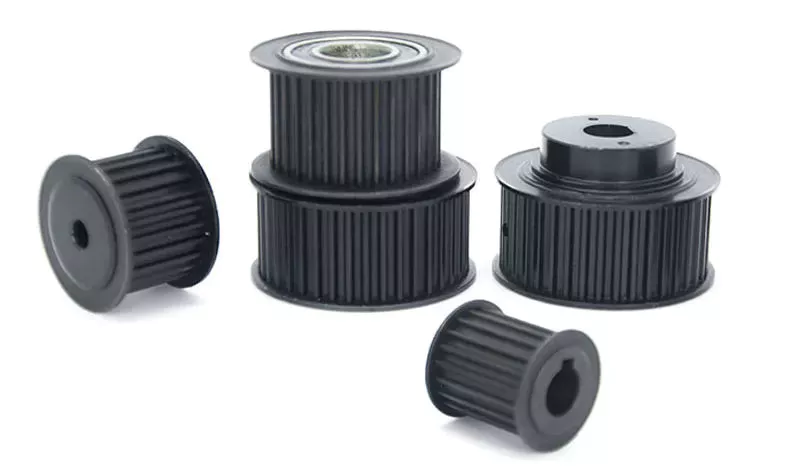

How do pulleys contribute to the operation of conveyor systems?
Pulleys play a critical role in the operation of conveyor systems by facilitating the movement of materials or products along the conveyor belt. Here’s how pulleys contribute to the functioning of conveyor systems:
1. Power Transmission: Conveyor systems typically utilize a motorized pulley, also known as a drive pulley or head pulley, which is connected to an electric motor. The motor rotates the drive pulley, which in turn moves the conveyor belt. The rotational power from the motor is transmitted to the belt through the drive pulley, enabling the continuous movement of the belt and the materials being conveyed.
2. Belt Tension and Tracking: Pulleys are used to maintain proper tension in the conveyor belt. Tension pulleys, also called idler pulleys, are strategically placed along the conveyor system to apply tension to the belt. These pulleys help to keep the belt taut and prevent slippage or sagging. Additionally, tracking pulleys are used to align the conveyor belt, ensuring it stays centered and runs smoothly along the intended path.
3. Load Support: Pulleys provide support for the conveyor belt and the load it carries. The belt wraps around the pulleys, and the load is distributed over the surface of the belt. Pulleys with larger diameters are often used at points where heavy loads are encountered to help distribute the load more effectively and prevent belt deformation or damage.
4. Directional Changes: Conveyor systems may require changes in direction to accommodate the layout or specific processing needs. Pulleys known as bend pulleys or snub pulleys are used to redirect the belt and change its course. These pulleys are designed to guide the belt smoothly around bends or corners without causing excessive stress or strain on the belt.
5. Speed Control: Pulleys can be utilized for speed control in conveyor systems. By using pulleys of different sizes or by employing variable speed drives, the rotational speed of the drive pulley can be adjusted, affecting the speed at which the conveyor belt moves. This allows for flexibility in the conveyance process, accommodating different material flow rates or specific operational requirements.
6. System Support and Stability: Pulleys, along with their associated support structures, provide stability to the conveyor system. They help to maintain the alignment and tension of the belt, preventing misalignment, vibrations, and excessive belt movement. Properly designed and maintained pulleys contribute to the overall reliability and smooth operation of the conveyor system.
Conveyor systems are widely used in industries such as manufacturing, mining, logistics, and warehousing. Pulleys are essential components that ensure the efficient and reliable movement of materials and products along the conveyor belt, enabling automated and continuous material handling processes.

How do pulleys work in garage door openers and winches?
Pulleys play a crucial role in both garage door openers and winches, enabling the smooth and efficient operation of these devices. They provide mechanical advantage, facilitate load lifting and lowering, and contribute to the overall functionality and safety of garage door openers and winches. Here’s how pulleys work in each of these applications:
1. Garage Door Openers:
In a typical garage door opener system, pulleys are used in conjunction with a motor, drive belt or chain, and a set of cables or torsion springs. The pulleys are mounted on the garage door’s torsion bar or header, and the cables or springs are connected to the bottom of the door. Here’s how the pulleys work in a garage door opener:
– Motor and Drive Mechanism: The motor drives a pulley or sprocket, which is connected to a drive belt or chain. As the motor rotates the pulley, the drive belt or chain moves, transferring rotational motion to another pulley or sprocket mounted on the torsion bar.
– Torsion Bar and Cables: The torsion bar, equipped with a pulley, is located above the garage door. The cables are threaded through the pulleys and attached to the bottom of the door on each side. When the motor rotates the torsion bar pulley, the cables move, causing the garage door to open or close.
– Mechanical Advantage: By using pulleys, the garage door opener system creates a mechanical advantage. The arrangement of the pulleys and cables or springs helps distribute the load, making it easier for the motor to lift the heavy garage door. This mechanical advantage reduces the strain on the motor and ensures smooth and controlled movement of the door.
2. Winches:
Pulleys are also integral components of winches used for lifting and pulling heavy loads. Winches consist of a drum or spool around which a cable or rope is wrapped, and pulleys are used to guide and redirect the cable or rope. Here’s how pulleys work in a winch:
– Load Lifting: The cable or rope is wound around the winch drum, and one end is attached to the load to be lifted or pulled. The other end is connected to a fixed point or a secondary pulley system. As the winch drum rotates, the cable or rope is wound or unwound, allowing the load to be lifted or lowered.
– Pulley Systems: Pulleys are used in winches to redirect the cable or rope, providing a mechanical advantage and ensuring smooth movement. Additional pulleys may be employed to create a block and tackle system, further increasing the mechanical advantage and the winch’s lifting capacity.
– Control and Safety: Winches often incorporate braking systems and clutches to control the movement and secure the load. Pulleys play a role in these control mechanisms, helping to regulate the winch’s speed and provide reliable stopping and holding power.
Overall, pulleys are essential components in garage door openers and winches, enabling the smooth and controlled movement of heavy loads. They provide mechanical advantage, facilitate load lifting and lowering, and contribute to the efficiency and safety of these devices.
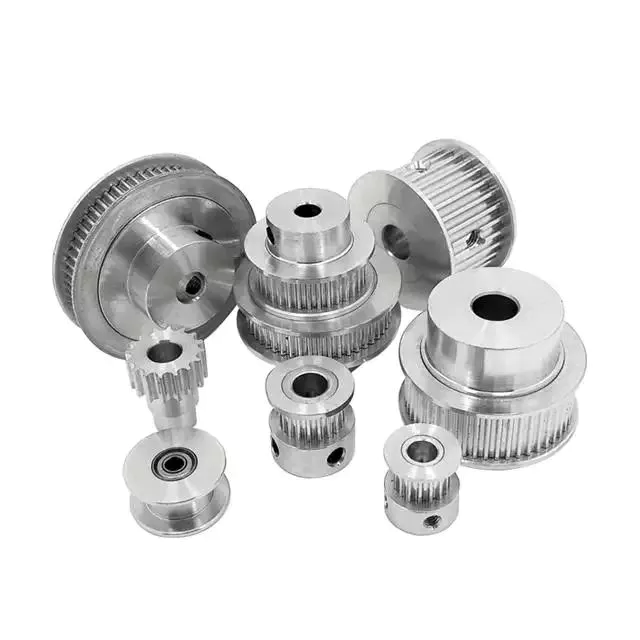

What are the different types of pulleys commonly used in industry?
Pulleys are widely used in various industries for different applications. Here are the different types of pulleys commonly used:
1. Fixed Pulleys: Fixed pulleys are attached to a stationary structure, such as a ceiling or wall. They change the direction of the force applied without providing any mechanical advantage. Fixed pulleys are often used in combination with other pulleys to create more complex systems.
2. Movable Pulleys: Movable pulleys are attached to the load being moved, and they move along with it. These pulleys provide mechanical advantage by reducing the effort required to lift the load. Movable pulleys are commonly used in systems such as block and tackle arrangements to lift heavy objects with less force.
3. Compound Pulleys: Compound pulleys consist of a combination of fixed and movable pulleys. They provide a greater mechanical advantage than a single pulley by distributing the load over multiple segments of the rope or belt. Compound pulley systems are often used in applications that require lifting extremely heavy loads.
4. Snatch Blocks: Snatch blocks are pulleys with a side plate that can be opened to insert or remove a rope or cable without threading it through the pulley. They are commonly used in rigging and towing applications to change the direction of force and create a mechanical advantage.
5. V-Belt Pulleys: V-belt pulleys have a V-shaped groove that matches the cross-section of V-belts. They are used in belt drive systems to transmit power between two shafts. V-belt pulleys are commonly found in applications such as industrial machinery, automotive engines, and HVAC systems.
6. Timing Pulleys: Timing pulleys have teeth that mesh with the teeth of a timing belt. They are used in synchronous drive systems to ensure accurate and synchronized power transmission. Timing pulleys are commonly used in applications such as robotics, printing presses, and CNC machines.
7. Rope Pulleys: Rope pulleys have a smooth surface designed to minimize friction and prevent wear on ropes. They are commonly used in applications where ropes are used for lifting or pulling, such as cranes, elevators, and material handling equipment.
8. Wire Rope Pulleys: Wire rope pulleys are specifically designed for use with wire ropes. They have grooves or pockets that accommodate the shape and size of wire ropes, ensuring secure grip and efficient force transmission. Wire rope pulleys are commonly used in applications such as cranes, winches, and hoists.
9. Idler Pulleys: Idler pulleys are used to guide and tension belts or ropes in a system. They do not transmit power but help maintain proper belt tension and alignment. Idler pulleys are commonly used in conveyor systems, automotive engines, and other belt-driven applications.
10. Sheave Pulleys: Sheave pulleys are large pulleys used in heavy-duty applications, such as crane systems and elevators. They are designed to handle high loads and provide smooth and reliable operation. Sheave pulleys often have multiple grooves to accommodate multiple ropes or belts.
These are some of the different types of pulleys commonly used in various industries. Each type has specific features and is selected based on the requirements of the application, such as load capacity, power transmission, and operational conditions.


editor by CX
2024-05-15